6 Memory Types in AI Agents: How Memory Makes AI Truly Intelligent
Introduction:
One thing that has changed over the years is AI, from simple chatbots that follow scripts. The secret behind an intelligent AI agent is memory, or the ability to recollect information and events from the past. Just like us, only with a better list, AI requires memory to learn, adapt, reason, and make future decisions based on context and prior experience.
In this article, we will cover the six key types of memory in AI agents — and how these change a chatbot into a knowledgeable digital agent.
The Importance of Memory in AI
Memory provides an AI system with the ability to think beyond the immediate input, and it can draw upon past conversations and experiences.
An AI agent must remember:
- To pull user preferences from memory
- To learn from the past
- To change behavior in association with that new learning
- To retain long-term goals and/or strategies
In essence, AI memory gives AI the ability to have a bridge between automation and intelligent behavior.
The Six Types of Memory in AI Agents
1. Short-Term Memory
Short-term memory is what allows an AI agent to temporarily store a small amount of information about recent events for an active session.
Key characteristics:
- Holding onto context in the short-term
- Supports natural conversational flow
- Resets after a session ends unless transferred to long-term memory
Example: It remembers that you’re currently discussing a project, but when the chat ends, it forgets that memory.
2. Long-Term Memory
Long-term memory allows the AI to store and retrieve information over time and lets the agent remember data about the user, the interactions, and any patterns in the conversations over a series of conversations and sessions.
Key characteristics:
- Provides persistent storage of memories
- Learns from past interactions
- A user can see personality and interactions being built over time
Example: It is the AI remembering that you like cats over dogs and will tailor responses based on that knowledge.
3. Semantic Memory
Semantic memory is everything the AI knows regarding factual knowledge or knowledge of concepts, or more plainly, what the AI knows about how things work, what things mean, or what a word means. You can think of this memory type as a sort of knowledge base inside the AI.
Key characteristics:
- It focuses on facts, rules, and relationships
- It’s used for inference and answering knowledge-based questions.
- It is essentially self-powered by the existence of either a vector database or a semantic knowledge base.
Example: It’s knowing that “Paris is the capital of France.”
4. Episodic Memory
Episodic memory enables your AI agents to remember an event, interaction, or a sequence of events that happened in the past. This is like a “memory of experiences” instead of just recording facts.
Key characteristics:
- Retains temporal or experience information
- Allows recollection of past events and learning
- Supports personalized and situational understanding
Example: The AI could remember that the user asked for project updates last Monday and provide a relevant response next time.
5. Procedural Memory
Procedural memory retains how-to knowledge, or the skills, steps, or procedures that enable the AI to perform work tasks automatically.
Key characteristics:
- Encodes patterns, skills, and operational routines
- Allows for automatic processing of repetitive tasks
- Improves efficiency and consistency of work tasks
Example: The AI can process refunds, generate reports, or translate sentences without being explicitly told how to do this with each task.
6. Declarative Memory
Declarative memory includes the storage of explicit information that can be recalled or communicated to one’s awareness. Declarative memory includes both semantic memory (stored facts) and episodic memory (stored experiences).
Key characteristics:
- Supports recall into consciousness
- Allows reasoning and explanation for knowledge retained
- Supports explainability of AI decisions
Example: The AI can explain why a specific decision was made as a reference to stored knowledge based on past facts and experiences.
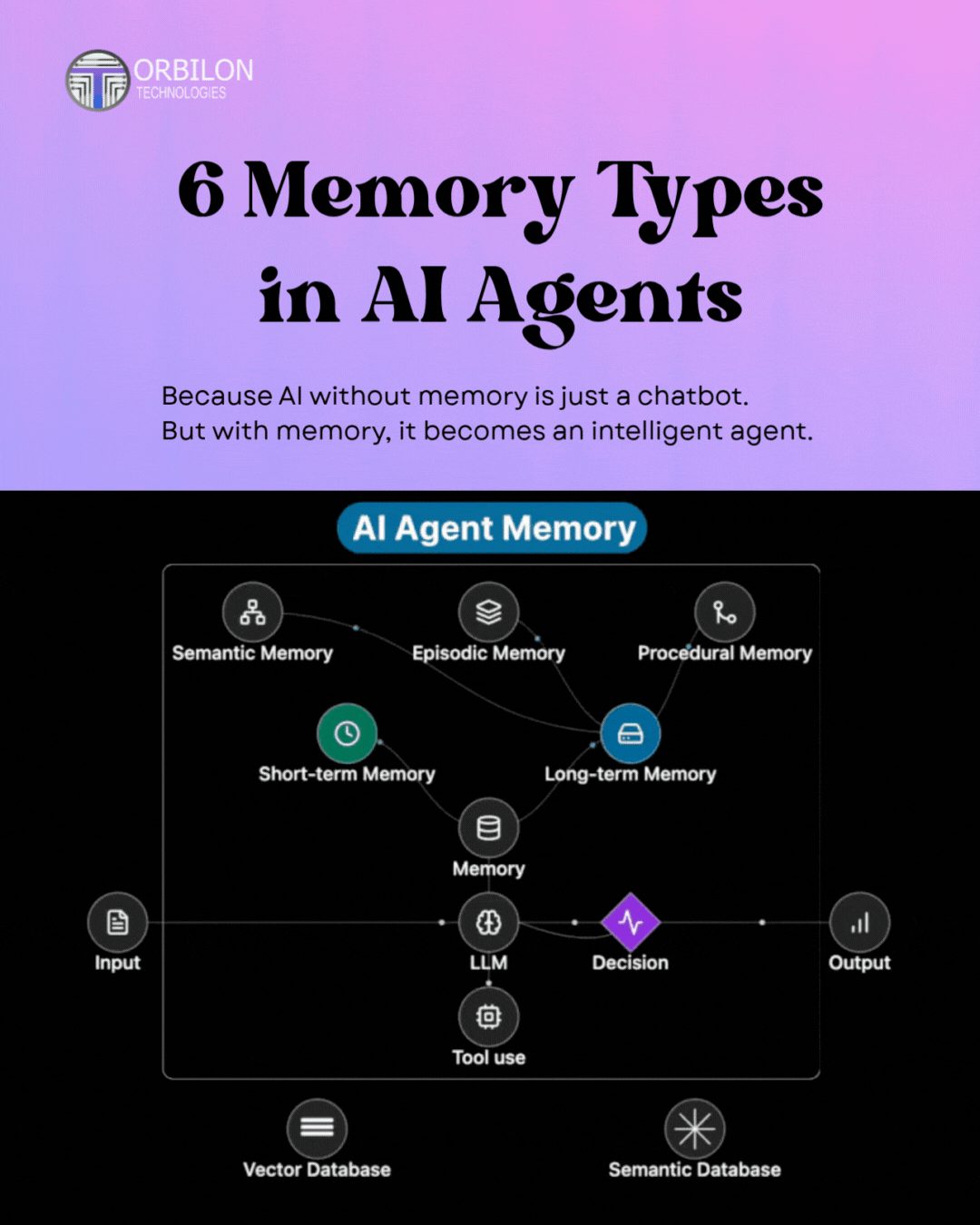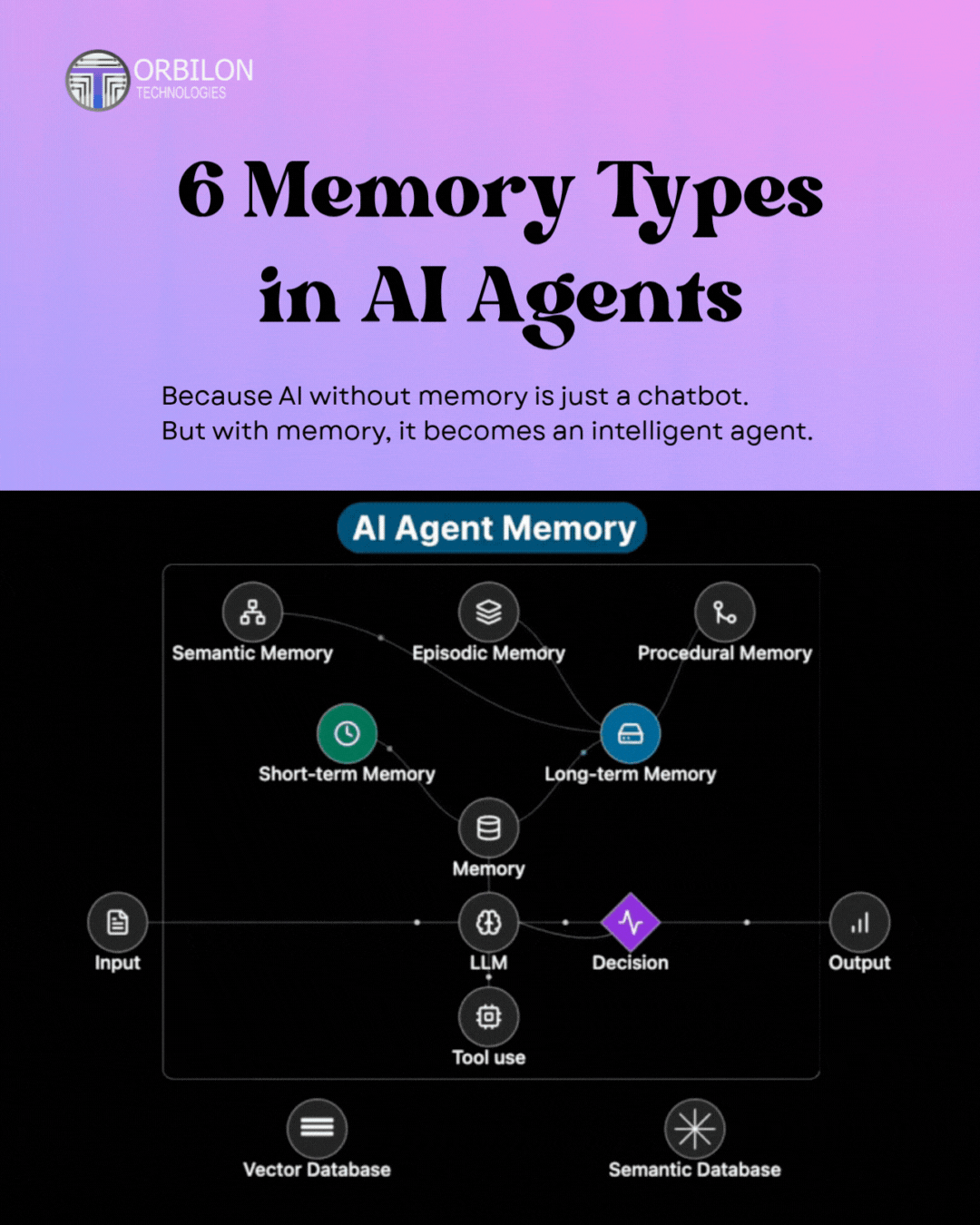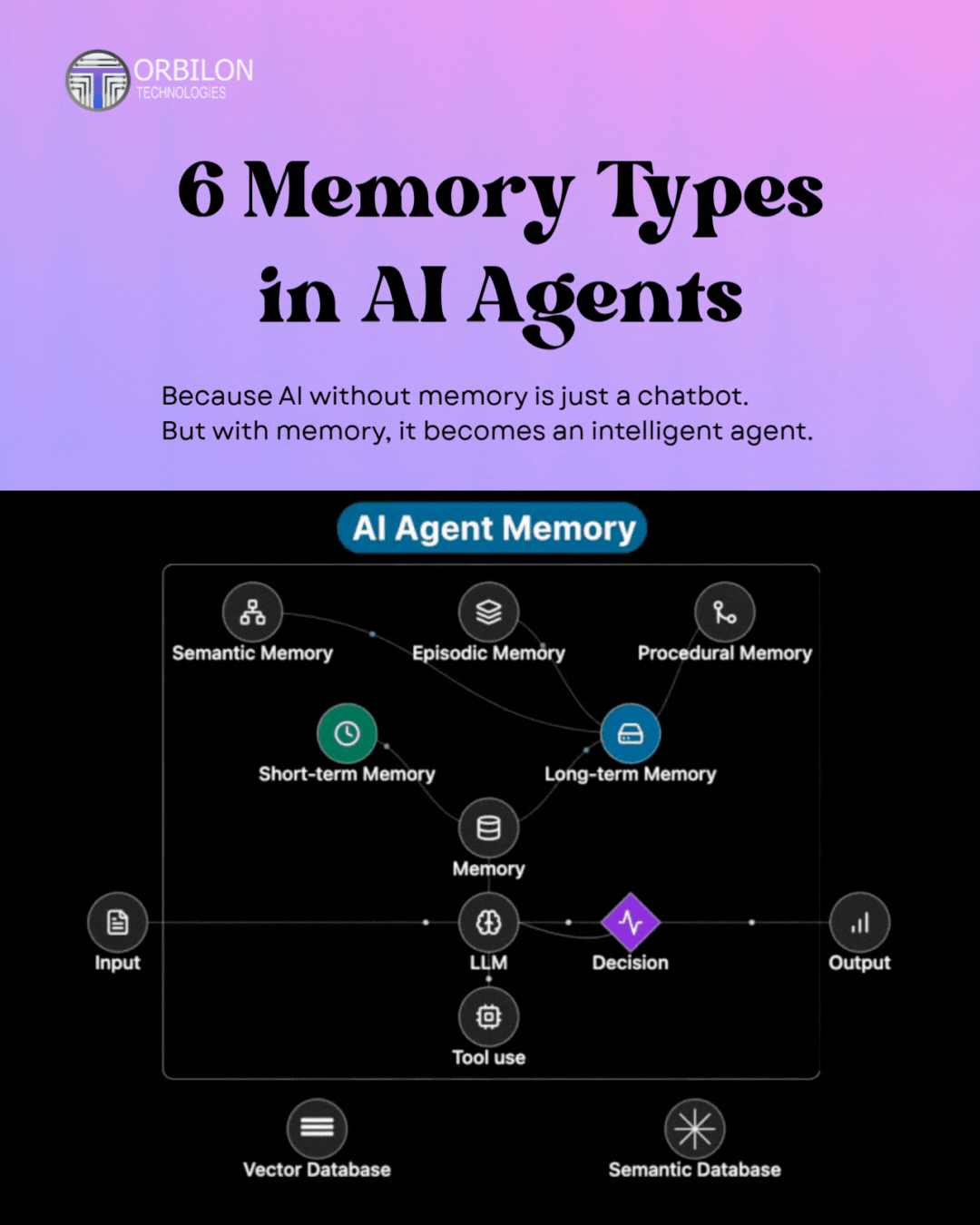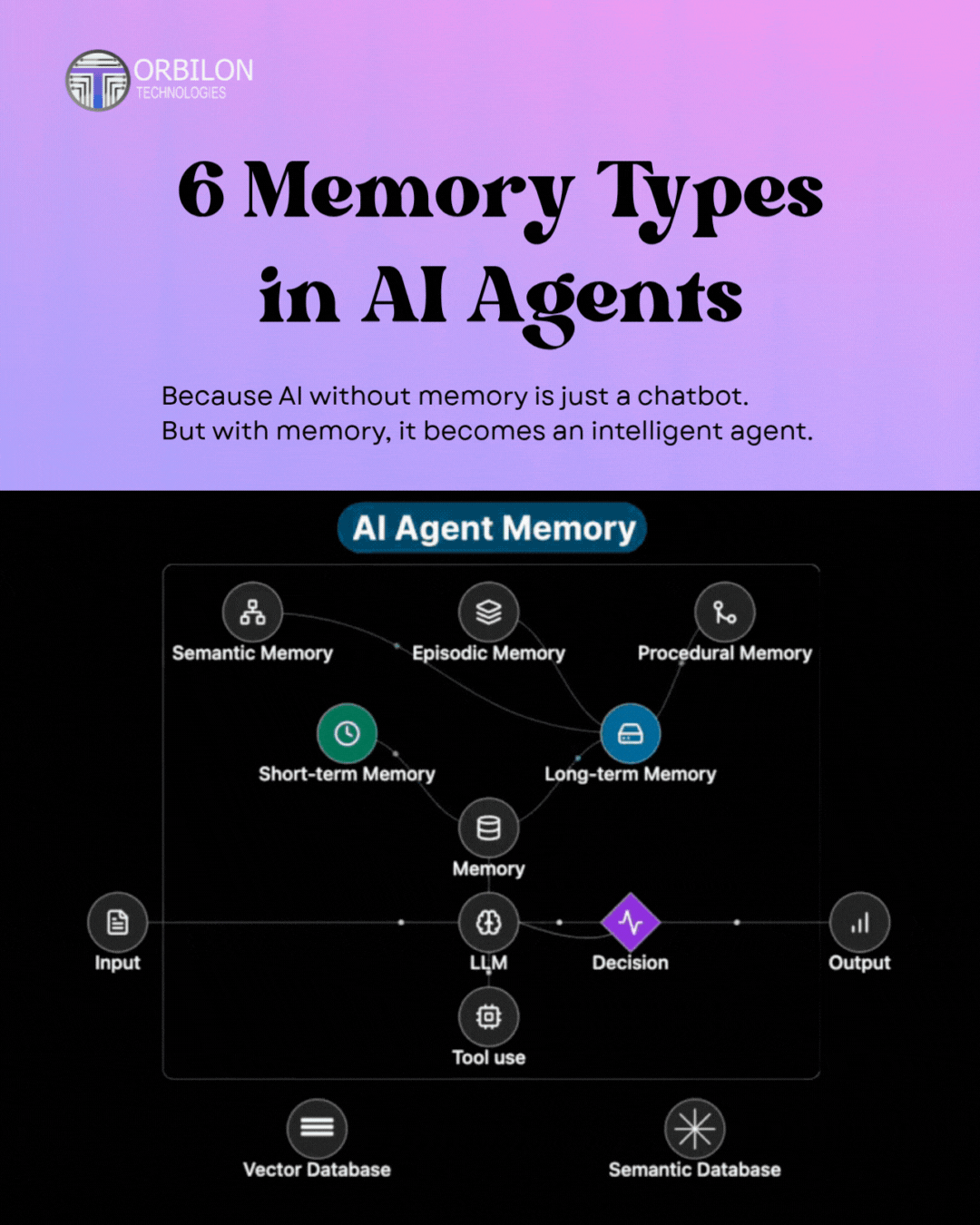
How These Memories Function Together
AI memory is layered from short- to long-term, connected by a database and LLMs.
In a simplified way, the flow is:
Input → Short-Term Memory → Long-Term Memory → Semantic/Episodic/Procedual Memory → LLM → Decision → Output
And there are a variety of supporting technologies:
- Vector Databases: Store semantic relationships between data.
- Semantic Databases: Support contextual reasoning.
- Tools: Enable AI to perform functions external to itself.
In addition, These factors together enable the agent to think, make decisions, and act intelligently.
Final Thoughts
An AI lacking memory is just a chatbot, typically reactive and unaware. Once memory is added to it, it turns into an intelligent agent, capable of learning, reasoning, and growing.
Moreover, the combination of different kinds of memory will drive or lead AI systems towards human-like abilities combined with digital precision, and will be part of the next generation of artificial thinking.
Want to Hire Us?
Are you ready to turn your ideas into a reality? Hire Orbilon Technologies today and start working right away with qualified resources. We will take care of everything from design, development, security, quality assurance and deployment. We are just a click away.