Traditional RAG Is DEAD
The RAG Revolution: GraphRAG | Agentic RAG | Contextual RAG
Technical Comparison 2026
Introduction
If your enterprise AI is still running on traditional RAG in 2026, you’re basically operating on a broken architecture. The GraphRAG vs traditional RAG argument has been settled: traditional systems only deliver 60-70% accuracy with 25-35% hallucination rates, while newer generation methods reach 88-95% accuracy.
Your AI is only as good as your RAG architecture.
And traditional RAG? It’s just not good enough anymore.
Why Traditional RAG Failed (And Why GraphRAG Won)?
Let us reveal the uncomfortable truth about the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems that most companies were using in 2023-2024.
The Four Fatal Flaws
1. 25-35% Hallucination Rate
Traditional RAG systems are infamous for their lack of truthfulness. When they are unable to retrieve relevant informationor even worse, partially relevant informationthey will go ahead and generate, quite confidently, answers that sound very plausible but are completely false.
In the context of enterprises where the accuracy of the information is of utmost importance, this is not just a minor inconvenience. It is a serious risk.
2. 60-70% Accuracy Ceiling
Even if traditional RAG doesn’t hallucinate, it still has a limit of accuracy around 60-70%. The question is why? The model treats each piece of information as separate and cannot connect the dots or reason across several related facts.
You might have a knowledge base with all the facts necessary to answer a question impeccably. However, if that information is spread through three documents with interdependent connections, traditional RAG will fail.
3. No Relationship Understanding
The main issue is that traditional RAG considers your data as isolated chunks in a vector database.
It doesn’t recognize:
- How concepts are related to one another.
- Which entities are linked?
- What dependencies exist between facts?
- How information flows through your company.
A human can reason: “If Policy A affects Process B, and Process B determines Outcome C, then Policy A ultimately impacts Outcome C.”
Traditional RAG cannot make this connection.
4. Context Fragmentation
During the embedding process, documents are split into smaller parts, which causes the loss of context at the boundaries of the parts. A paragraph may refer to “the aforementioned policy” or “this methodology,” but if these references are in different parts, RAG retrieves fragmented, incomplete information.
The result? Replies that are correct in a technical sense for the retrieved parts but are ipso facto meaningless in a larger context.
Why This Matters in 2026?
In 2023 and 2024, companies still had room to tolerate these limitations. AI was simply a novelty, people had lower expectations, and just having any RAG system was considered state, of, the, art.
That’s no longer the case.
In 2026, AI systems that hallucinate 30% of the time or miss the main context will not only be considered as underachievingthey will be viewed as violators of trust, creators of legal risks, and losers to those competitors that have already moved on to next-generation architectures.
The Three Next-Generation RAG Architectures
The positive thing is that three revolutionary RAG approaches have surfaced, which address the fundamental limitations of conventional RAG:
- GraphRAG: The new standard for connected knowledge.
- Agentic RAG: The powerhouse for complex reasoning.
- Contextual RAG: The emerging star for precision.
1. GraphRAG: The Way to Go
How It Works
Instead of just throwing data bits into a vector database, GraphRAG creates a knowledge graph. Think of it like this: things are nodes, and how they relate are the edges.
Traditional RAG:
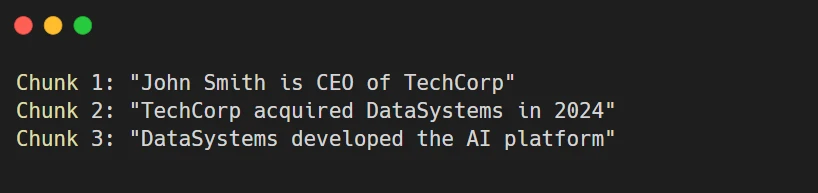
- Query: “Who leads the company that owns the AI platform?”
- Traditional RAG: Struggles to connect these isolated facts.
GraphRAG:
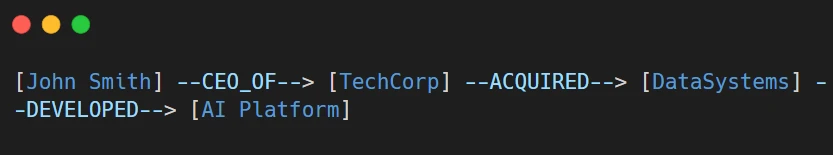
- Query: “Who leads the company that owns the AI platform?”
- GraphRAG: Traverses the graph → John Smith (CEO) → TechCorp → acquired DataSystems → developed AI Platform.
- Answer: “John Smith, as CEO of TechCorp, leads the company that owns the AI platform through TechCorp’s acquisition of DataSystems.”
The GraphRAG Process
Step 1: Knowledge Graph Construction
Documents are analyzed to extract:
- Entities: People, companies, products, policies, processes.
- Relationships: Reports to, affects, depends on, precedes, causes.
- Attributes: Properties, metadata, timestamps.
- A structured representation of your knowledge is thus formed.
Step 2: Relationship Traversal
GraphRAG doesn’t just retrieve similar pieces when a query arrives. Rather, it:
- Determines which entities in the query are relevant.
- Look for those entities in the knowledge graph.
- Explores relationships to find information that is connected.
- Moves along multi-hop paths in the graph.
Step 3: Context-Aware Retrieval
Retrieval of information may contain not only the direct answer but also the whole context:
- Related entities.
- Connecting relationships.
- Dependency chains.
- Supporting evidence.
Step 4: Explainable Generation
The LLM produces an answer that can be completely traced:
- Which nodes were accessed?
- What relationships were traversed?
- Why was specific information included?
- How the conclusion was reached.
GraphRAG Performance
- Accuracy: 80-85%.
- Hallucination Rate: 10-15%.
- Explainability: High (graph paths show reasoning).
- Relationship Understanding: Excellent.
Best Use Cases
a. Enterprise Knowledge Bases
Information from multiple departments with complex interconnections. GraphRAG answers such questions very well as:
- “Which policies regulate this process in all the departments?”
- “How will this decision affect downstream operations?”
- “Who are all the stakeholders?”
b. Compliance Systems
Regulatory requirements that have very complex interrelations between rules, processes, and obligations:
- “Which regulations govern this particular case?”
- “What compliance impacts happen if we modify Process X?”
- “Show me the line of reasoning in the audit from the action to the requirement”.
c. Research Platforms
Scientific papers, references, and related concepts:
- “Which research is used to support this hypothesis in different papers?”
- “How has this theory changed over time?”
- “What methods link these results?”
d. Connected Data
A domain where the relationships between the entities are of great importance:
- Supply chain dependencies.
- Organizational hierarchies.
- Technical system architectures.
- Customer relationship mapping.
GraphRAG Limitations
- Complexity: The construction and maintenance of knowledge graphs requires a lot of engineering work.
- Update Challenges: Changing one entity might necessitate the reprocessing of the parts of the graph that are connected to this entity.
- Computational Cost: Performing a graph traversal or community detection is more costly than a basic vector search.
- Brittleness: The graph structure can easily be damaged if there are too many changes, so it needs to be properly maintained.
2. Agentic RAG: The Powerhouse
How It Works
Agentic RAG considers retrieval a dynamic planning and reasoning activity, rather than a passive lookup.
Instead of:
- Retrieve chunks.
- Send to LLM.
- Generate an answer.
Agentic RAG does:
- AI agent analyzes the query.
- Plans retrieval strategy (which sources, what order).
- Executes multi-source retrieval (databases, APIs, knowledge graphs).
- Iteratively refines based on what it finds.
- Verifies output before responding.
- Self-corrects if verification fails.
Imagine replacing your AI’s search engine with a research team.
The Agentic RAG Process
Step 1: Query Decomposition
The Agent splits a complex query into smaller sub-tasks:
Query: “Analyze our Q4 financial risk from supply chain disruptions”
Agent plans:
- Get Q4 financial projections.
- List key suppliers.
- Look up supply chain issues in the news.
- Check supplier dependencies.
- Work out risk exposureCreate risk assessment.
Step 2: Multi-Source Retrieval
The agent uses a variety of different and independent resources:
- Internal financial databases.
- Supply chain management system.
- News APIs.
- Historical incident data.
- Industry reports.
- Every retrieval was sharply focused and had a specific goal.
Step 3: Iterative Refinement
The Agent rechecks and re-evaluates its answer, drafting the approach and tool usage with a set of self-posed questions and by uncovering new revelations:
- Obtains data for the initial response.
- Points out inconsistencies or gaps.
- Retrieves extra contextual information.
- Checks the accuracy of the final findings.
Step 4: Verification and Self-Correction
Before responding, agent:
- Cross-checks facts across sources.
- Validates calculations.
- Identifies confidence levels.
- Flags uncertainties.
- Corrects errors discovered during verification.
Step 5: Explainable Output
Final answer includes:
- Reasoning trace.
- Sources consulted.
- Confidence levels.
- Limitations or caveats.
Agentic RAG Performance
- Accuracy: 85-92%.
- Hallucination Rate: 5-8%.
- Self-Correction: Excellent.
- Multi-Step Reasoning: Superior.
- Computational Cost: High.
Best Use Cases
i. Legal Research
Complex legal queries requiring analysis across statutes, case law, and precedent:
- What are the legal precedents applicable to this situation?
- How has the interpretation of this law evolved?
- What are our compliance obligations given recent rulings?
ii. Medical Diagnosis Support
Assist in clinical decision-making by relying on a wide- ranging medical knowledge base, including:
- Searching through medical literature for symptom matching,
- Checking medicines for potential interaction.
- Suggesting treatments supported by evidence.
- Writing diagnostic reasoning chains.
iii. Financial Analysis
Thorough financial investigation and risk evaluation of complex cases:
- Deep market analysis based on multiple data sources.
- Risk model development with consideration of various scenarios.
- Checking for compliance with a range of regulations.
- Conducting investment research and cross-checking.
iv. Strategic Decision-Making
Making critical decisions based on thorough, comprehensive analyses:
- Evaluating potential market opportunities.
- Gathering competitive intelligence.
- Strategic planning by using different scenario models.
- Performing extensive research for due diligence.
Agentic RAG Limitations
- Latency: Multi-step reasoning takes seconds to minutes vs. milliseconds.
- Cost: Multiple LLM calls and retrieval operations increase expense.
- Complexity: Requires sophisticated agent orchestration frameworks.
- Unpredictability: Agent behavior can be harder to control than simple RAG pipelines.
3. Contextual RAG: The New Rising Star
How It Works
Contextual RAG tackles the issue of context fragmentation by keeping the document’s structure and the relationships between parts intact, even when chunking and embedding.
Traditional RAG chunking:
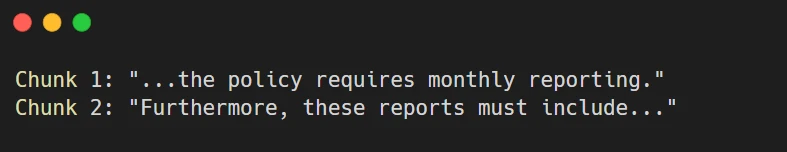
Lost context: What policy? What reports?
Contextual RAG chunking:
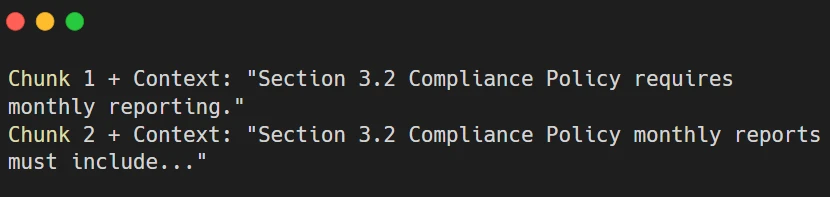
Preserved context: Every chunk knows what document, section, and topic it belongs to.
The Contextual RAG Process
Step 1: Document Context Preservation
- Contextual RAG, during ingestion:
- Maintains document hierarchies.
- Preserves section structures.
- Tracks cross, references.
- Retains metadata chains.
Step 2: Chunk Boundary Awareness
- The chunking algorithm understands:
- Semantic boundaries (where topics change).
- Structural boundaries (sections, chapters).
- Reference boundaries (citations, links).
- Dependency boundaries (definitions, prerequisites).
- Chunks are generated at natural boundaries rather than arbitrary character counts.
Step 3: Contextual Embeddings
The embedding of each chunk is made up of:
- The chunk text itself.
- Surrounding context (document, section, topic).
- Hierarchical position.
- Related chunks.
Step 4: Exact Retrieval
Retrieval finds not merely semantically similar chunks, but contextually appropriate chunks:
- Right section of the right document.
- Appropriate level of detail.
- Complete context included.
- No broken references.
Contextual RAG Performance
Accuracy: 88, 95%Hallucination Rate: 3, 5%Speed: Fast (comparable to traditional RAG)Precision: ExceptionalContext Preservation: Superior.
Best Use Cases
a. Technical Documentation
Code documentation, API references, system architectures:
- “How do I implement this specific feature?”
- “What are the dependencies for this function?”
- “Show me examples in context.”
b. Code Search
Finding code across large codebases:
- Function definitions with full context.
- Usage examples with complete implementations.
- Debugging assistance with the surrounding code.
c. Precise Q&A
Examples of situations where the requirement of a very precise and unambiguous answer applies:
- Interpretation of the provisions of a contract between the parties.
- Determining the exact requirements of a regulatory authority.
- Technical specifications.
- Standard operating procedures.
d. Domain-Specific AI
Specialized AI systems where precision matters more than breadth:
- Medical protocols and guidelines.
- Engineering standards and specifications.
- Scientific methodology documentation.
- Financial regulatory frameworks.
Contextual RAG Limitations
- Initial Setup: Needs a thorough analysis of the document structure.
- Domain-Specific: Performs best with structured, hierarchical content.
- Less Flexible: Not suitable for unstructured or very diverse data sources.
- Metadata Overhead: Extra storage space needed for contextual data.
GraphRAG vs Traditional RAG: Head-to-Head Comparison
i. Accuracy Battle
- Traditional RAG: Accuracy ranging between 60 and 70%.
- GraphRAG: Accuracy ranging between 80 and 85% + 15-20% accuracy improvement over traditional.
- Agentic RAG: Accuracy between 85 and 92% + 25-32% improvement over traditional.
- Contextual RAG: Accuracy between 88 and 95% + 28-35% improvement over traditional.
Winner: Contextual RAG (by a narrow margin), but all three next-gen approaches outperform traditional RAG massively.
ii. Hallucination Reduction
- Traditional RAG: 25-35% hallucination rate.
- GraphRAG: 10-15% hallucination rate – 60% hallucination reduction.
- Agentic RAG: 5-8% hallucination rate – 77% hallucination reduction.
- Contextual RAG: 3-5% hallucination rate – 86% hallucination reduction.
Winner: Contextual RAG with dramatically lower hallucination rates.
iii. Speed and latency
- Traditional RAG: Milliseconds (baseline).
- GraphRAG: 100-500ms (graph traversal overhead)
- Agentic RAG: 1-30 seconds (multi-step reasoning).
- Contextual RAG: Milliseconds (comparable to traditional RAG).
Winner: Contextual RAG keeps up the speed of traditional RAG while providing better accuracy.
iv. Implementation Complexity
- Traditional RAG: Low (vector DB + embeddings).
- GraphRAG: High (knowledge graph construction and maintenance).
- Agentic RAG: Very High (agent orchestration, multi-source integration).
- Contextual RAG: Medium (document analysis, contextual chunking).
Winner: Traditional RAG (although this is pretty much its only advantage left).
v. Cost
- Traditional RAG: Lowest (simple retrieval, single LLM call).
- GraphRAG: Medium, High (graph construction, complex queries).
- Agentic RAG: Highest (multiple LLM calls, diverse tool usage).
- Contextual RAG: Low, Medium (additional storage, similar retrieval cost).
Winner: Traditional RAG, but at what cost to accuracy?
Which one to use when:
Go for GraphRAG if:
- The interplay of data is vital.
- You want your reasoning process to be very clear.
- Multi-hop questions are the norm.
- The data is naturally interwoven.
Go for Agentic RAG if:
- Accuracy is the top priority.
- There is a readiness to accept latency and cost for the luxury.
- The questions are complicated and have several aspects.
- Realizing the value of self, correction is an important factor.
Go for Contextual RAG if:
- The structure of the document is very clear.
- You care more about checking accuracy than about covering a large area.
- Speed is essential to you.
- Content is hierarchical or technical.
Never choose Traditional RAG:
- Unless you’re literally deploying a minimum viable prototype.
- Even then, start with Contextual RAG—it’s almost as simple.
Real-World Migration Results: Orbilon Technologies
At Orbilon Technologies, we’ve carried out the change of 12 enterprise clients from the traditional RAG to the next-gen architectures with the help of the newest deep learning methods in the past 3 months.
The Numbers
- 12 Clients Migrated. Moved from traditional RAG to Graph RAG, Agentic RAG, or Contextual RAG.
- +43% Average Accuracy GainAcross all clients and use cases.
- 67% Hallucination Reduction, almost eliminated false information.
- +89% User Satisfaction Teams trust the AI again.
- 4-10x ROI in Year One. Productivity gains, error reduction, time savings.
Timeline
- Week 1 to 2: Assessment and architecture design.
- Week 3 to 6: Knowledge graph construction or contextual processing.
- Week 7 to 8: Integration and testing.
- Weeks 9 to 12: Deployment and optimization.
- Total: 8 to 12 weeks from assessment to production
Investment
- Small Deployment (1-2 systems, <1M documents): $20-30K.
- Medium Deployment (Multiple systems, 1-10M documents): $30-40K.
- Large Deployment (Enterprise, wide, 10M+ documents): $40-50K
+Annual Value Delivered.
Conclusion: GraphRAG vs Traditional RAG - The Clear Winner
It’s almost ridiculous to argue GraphRAG vs traditional RAG. Traditional RAG is done and dusted. Not “in decline” or “being slowly phased out”, dead.
In 2026, rolling out traditional RAG would be like publishing a website that only works on Internet Explorer 6. Yes, it’s doable, but from a professional point of view, it’s indefensible.
The alternatives GraphRAG, Agentic RAG, and Contextual RAGare not just marginally better. They are in a totally different league:
- 80-95% accuracy vs. 60-70%.
- 3-15% hallucinations vs. 25-35%.
- Relationship understanding vs. isolated chunks.
- Explainable reasoning vs. black boxes.
The issue is not whether to upgrade. It is how fast can you do it?
Your competitors are already making their moves. Your users’ trust in hallucinating AI is eroding. Your enterprise is creating value that you can’t capture using broken retrieval methods.
The technology is there.
The migration path is well established.
The ROI is obvious.
Are you ready?
About Orbilon Technologies
Orbilon Technologies is a leader in providing next-generation AI architecture solutions to businesses. We create agentic AI systems, implement autonomous workflows, etc. We also integrate AI with existing infrastructures and develop production-ready solutions that bring real business value.
We are experts in GraphRAG deployment, Agentic RAG orchestration, Contextual RAG implementation, and hybrid architecture design. In the past 90 days, we’ve enabled 12 enterprise clients to migrate successfully, and on average, their accuracy has gone up by 43%, with hallucination down by 67%.
Contact: support@orbilontech.com
Website: https://orbilontech.com
Want to Hire Us?
Are you ready to turn your ideas into a reality? Hire Orbilon Technologies today and start working right away with qualified resources. We will take care of everything from design, development, security, quality assurance and deployment. We are just a click away.

